- May 1, 2022
- By: Arias Hospital Nashik
Urinary Incontinence: Types, Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment
The number of people suffering from bladder issues is constantly increasing. Though Urinary Incontinence is not a disease in itself, it can a symptom of any unnoticed medical issue. So, getting it diagnosed is a must. Here is what you need to know about Urinary Incontinence.
What is Urinary Incontinence?
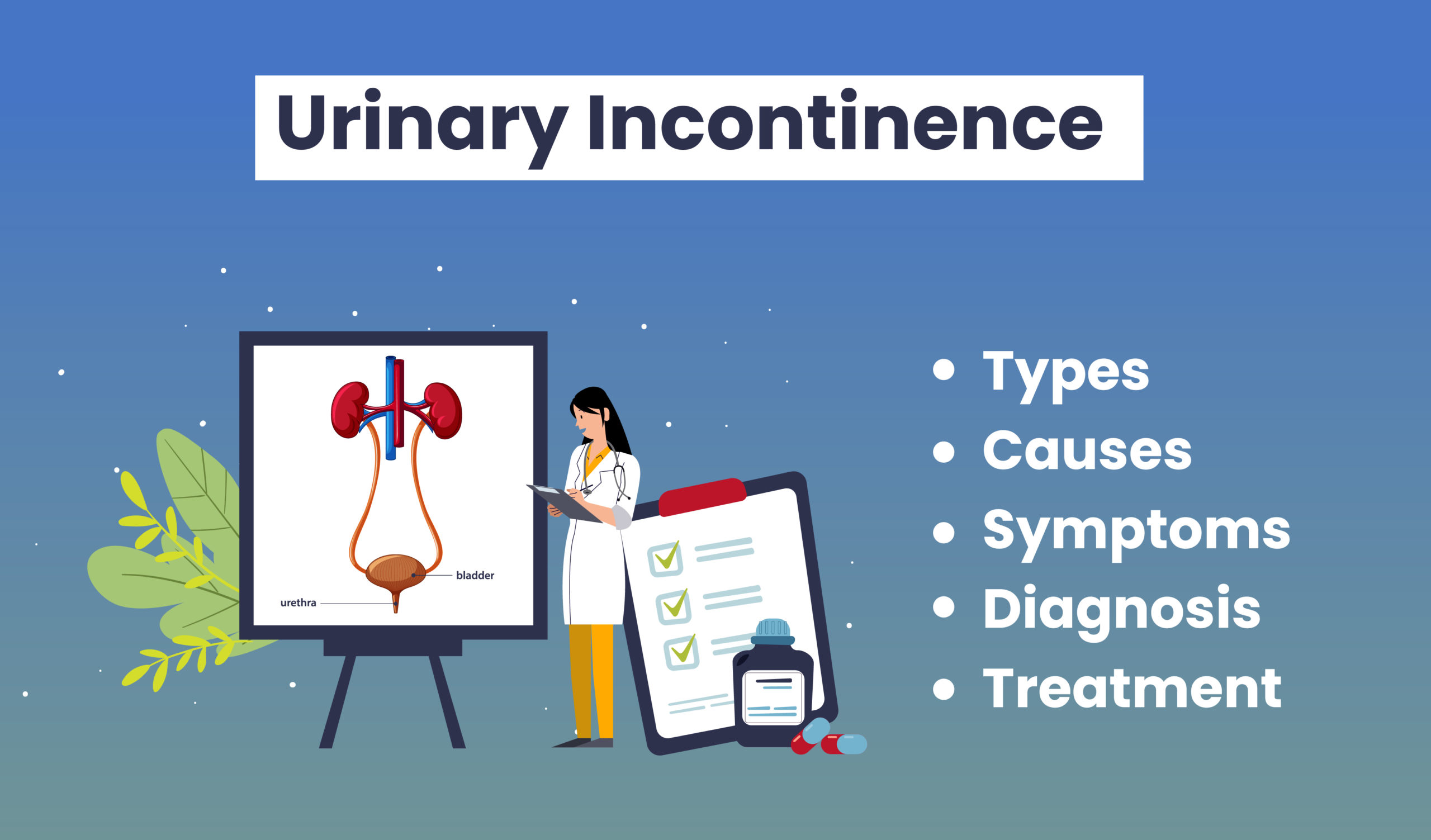
Urinary incontinence is the involuntary leakage of urine from the bladder that a person cannot prevent. It basically happens when the muscles in the bladder, responsible to control the flow of urine, contract or relax involuntarily, or the control over the urinary sphincter is either lost or weakened.
The severity of this condition can range from occasional leakage due to coughing and sneezing to having a sudden urge to urinate that you cannot even make it to the toilet.
Types of urinary incontinence
Incontinence is differentiated into several different types depending on the cause, characteristic, and trigger for urine leakage such as:
- Urge Incontinence:
The strong and intense need to urinate is the characteristic of this type. The urge is so sudden that the person cannot even make it to the toilet and end up leaking urine. This condition is caused by an overactive bladder (OAB) that is a result of weak pelvic muscles, nerve damage, infection, low levels of estrogen after menopause, obesity, or due to some medications and beverages like alcohol and caffeine.
- Stress incontinence:
Urine leakage is caused during activities is often termed stress incontinence. In this type, the pelvic floor muscles are too weak to support the pelvic organs as they should. Hence, a person is more likely to leak urine accidentally while moving around, laughing, coughing, sneezing, running, jumping, or lifting things.
- Overflow Incontinence:
When the bladder doesn’t empty itself completely each time while urinating, it is often regarded as overflow incontinence. We can understand this with an example of a glass filled with water. Think, you only emptied the half glass and the rest is still filled with water. So, if you move with that half-filled glass, there is always the risk of spilling the water. The same concept is applicable here. Hence, people with overflow incontinence are always at risk for leakage. However, the leakage is in small amounts instead of one big gush.
- Mixed Incontinence:
When a person deals with more than one of the above-listed issues, he or she is dealing with mixed incontinence. The person can even have stress incontinence with an overactive bladder of this type. Hence, it is crucial to figure out the issues that trigger this incontinence to manage it in a better way.

Who is at the risk of developing incontinence?
Anyone can develop incontinence. However, it is more common among women than in men. Mainly because the urethra in women is shorter than in men and women also undergo various events in life like pregnancy, childbirth, and transition through menopause. Each of these events has a great impact on her bladder ultimately leading to urinary incontinence.
Pregnancy causes short-term issues that eventually get better after giving birth. However, some women experience incontinence after the baby is born due to the strain caused on pelvic floor muscles. Even Menopause brings a lot of changes in the woman’s body that can alter bladder control.
Even old people are at risk of developing this condition. With increasing age, the body gets weaker, and thus the ability of the muscles to support your pelvic organs leads to urinary incontinence. People with weakened muscles are more likely to experience leakage.
What Causes Incontinence?
There are multiple underlying medical conditions and physical problems that can lead to temporary or persistent urinary incontinence states the experts from the best maternity hospital in Nashik. They include:
Causes for temporary urinary incontinence
- Certain foods, and drinks like alcohol, caffeine, carbonated drinks, artificial sweeteners, chocolate, chili peppers, spicy foods, and large doses of Vitamin C.
- Medications like blood pressure medications, sedatives, and muscle relaxants may act as diuretics, stimulate your bladder, and increase the volume of your urine.
- Urinary tract infections irritating your bladder
- Constipation
Causes for persistent urinary incontinence
- Hormonal changes and increased weight of the fetus in pregnancy can lead to stress incontinence.
- Vaginal delivery can weaken the bladder muscles or damage the nerves and supportive tissue leading to the dropped pelvic floor.
- Age is another factor that can lead to urinary incontinence due to the weakening of muscles.
- Less production of estrogen (a hormone responsible to maintain the health of the lining of the bladder and urethra) after Menopause.
- The enlarged prostate gland in older men also often leads to incontinence.
- Untreated prostate cancer
- A tumor anywhere along the urinary tract blocking the normal flow of urine
- Disorders like Sclerosis, Parkinson’s disease, stroke, brain tumor, or spinal injury disturb the signals involved in bladder control.
- Being overweight as it increases the pressure on the bladder and its muscles eventually weakening them.
- Consistent use of tobacco may also increase the risk of urinary incontinence.
How is Urinary Incontinence Diagnosed?
The diagnosis will start with a basic conversation about your medical history and some questions regarding your bladder control issues like:
- How often do you urinate?
- Do you leak urine between trips to the toilet?
- How often does this happen?
- How long have you been dealing with this condition?
These questions help the doctor figure out the type of incontinence you have and suggest the treatment accordingly.
The doctor will most likely recommend you:
- Urine Analysis Test (to check the sample of urine for infections),
- To maintain Bladder Diary (to check the frequency of intake of water, urination, urge to urination, and incontinence episodes), and
- To measure post residual volume of urine (to check for any obstruction in your urinary tract).
You may also need to go for tests like Urodynamic testing, and pelvic ultrasound, if the doctor requires any further information.

How to Treat Incontinence?
The doctor will tailor your treatment plan according to the type of incontinence you have and the way it affects your life. Here we have discussed some of the most common methods recommended for improving Urinary Incontinence.
Lifestyle changes
In most cases, urinary incontinence can be easily treated by making some changes such as:
- Emptying the bladder regularly (time voidings).
- Emptying the bladder before performing any physical activities.
- Not lifting heavy objects.
- Exercising regularly with Kegel’s Exercises to help strengthen your pelvic floor muscles.
- Avoid caffeine and other fluids before beginning any activity and before going to bed.
- Wearing pads or products designed to catch leakage in order to maintain incontinence.
- Practicing bladder training
- Maintaining a healthy weight.
Medications
- Anticholinergics: taken to calm the overactive bladder
- Mirabegron: helpful in the treatment of urge continence by relaxing the bladder muscle
- Alpha-blockers: helpful in relaxing the bladder neck muscles and muscle fibers in the prostate to make it easier for men to empty the bladder.
- Topical Estrogen: low-dose application of vaginal cream or patch may rejuvenate and tone the tissues in the urethra and vaginal areas.
Medical Devices:
The following are some devices that help improve urinary incontinence in women:
- Urethral insert: It is a small tampon-like device inserted into the urethra before performing any activity that triggers the incontinence to prevent leakage.
- Pessary: It is a flexible silicone ring designed to insert into the vagina to support the urethra and prevent urine leakage. It is also helpful for women with vaginal prolapse.
Surgeries
If other procedures don’t work, the doctor may recommend you any of the following surgery.
- Sling procedure: Here a synthetic material is inserted underneath your urethra to keep it closed while you cough or sneeze. This procedure is helpful for treating stress incontinence.
- Bladder Neck Suspension: This procedure is performed to support the urethra and bladder neck.
- Prolapse Surgery: The prolapse surgery is usually combined with a sling procedure to help improve the urinary incontinence symptoms.
- Artificial Urinary Sphincter: This procedure is performed to keep the sphincter shut by implanting a small, fluid-filled ring around the bladder neck until there is a need to urinate.
Urinary Incontinence is an important health issue that has negatively impacted the lives of many. People in India usually prefer to not talk about it due to the stigma surrounding it. Plus, they withdraw themselves socially eventually paving the way to depression. Hence, our best gynecologist in Nashik at ARiAS, highly recommend discussing your incontinence issues with an expert.